Alkene Vs Alkyne Stability
The bond energy of an average C-C single bond is around 347 kJmol and C-H bond around 308435 kJmol both of which need a relatively high energy to break. Stability is simply a measure of energy.
They have a lower heat of hydrogenation.

Alkene vs alkyne stability. Geometry and rotation about the double bond and stability of differently substituted forms. The key difference between alkenes and alkynes is that the alkenes have carbon-carbon double bonds whereas the alkynes have carbon-carbon triple bonds. As with alkenes the more highly substituted internal alkynes are more stable.
So they are less reactive when compared to alkenes in general. Alkynes are less stable then alkenes and alkanes despite the bond being stronger. But many reactions proceed through high-energy cation or free radical intermediates.
The stability differences are accounted for by the delocalization of electron density towards the R groups. Alkenes are more reactive than their related alkanes due to the relative instability of the double bond. The main difference between alkanes and alkenes is that alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons whereas alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
Both these types of hydrocarbons are composed of branched unbranched and cyclic hydrocarbons. There can be other substituents attached to these molecules instead of hydrogens. In alkanes there are only bonds i.
By comparing thermodynamic data of alkynes and alkenes it can be seen that the extra bond in an alkyne is weaker than the alkene bond. Internal alkenesalkynes are more stable than terminal ones because when the bond is internal and connected to more than one carbon-secondary tertiary quaternary-- the pi bonds are more stabilized by the surrounding carbons. Generally speaking alkenes are less stable than alkanes.
Alkanes have a single bond less energy than alkenes and alkynes which have respectively two and three bonds and higher energy. Collectively they are called unsaturated hydrocarbons which are defined as hydrocarbons having one or more multiple double or triple bonds between carbon atoms. Also internal alkenes are more stable than terminal ones.
Alkene and Carbocation Stability Alkene Stability R R R R H R R R H H R R R H H R H R TetrasubstitutedTrisubstituted Disubstituted Trans Cis Monosubstituted General Rules. Conjugated dienes have enhanced stability due to resonance. Alkenes can also be reacted typically in.
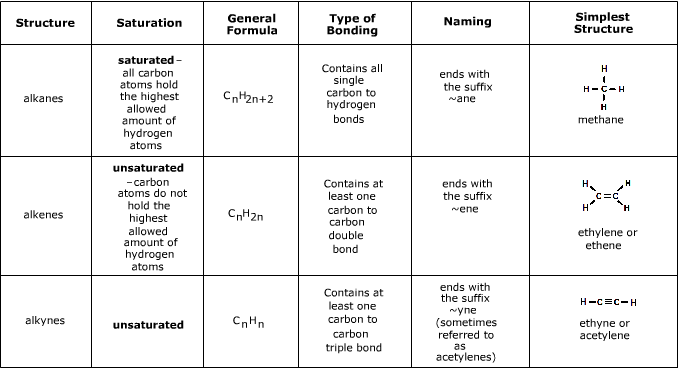
They are more likely to participate in a variety of reactions including combustion addition hydrogenation and halogenation reactions. Both alkenes and alkynes are hydrocarbons having carbon and hydrogen atoms. Structure and Stability Degrees of unsaturation saturated hydrocarbon CnH2n2 cycloalkane 1 ring CnH2n alkene 1 p-bond CnH2n alkyne 2 p-bonds CnH2n-2 For each ring or p-bond -2H from the formula of the saturated alkane Degrees of unsaturation.
In these cases the resonance stabilization of the intermediate allyl species makes conjugated dienes much more reactive than alkenes. Alkanes and alkenes are such two categories. Higher energy means shorter bonds which means stronger bonds.
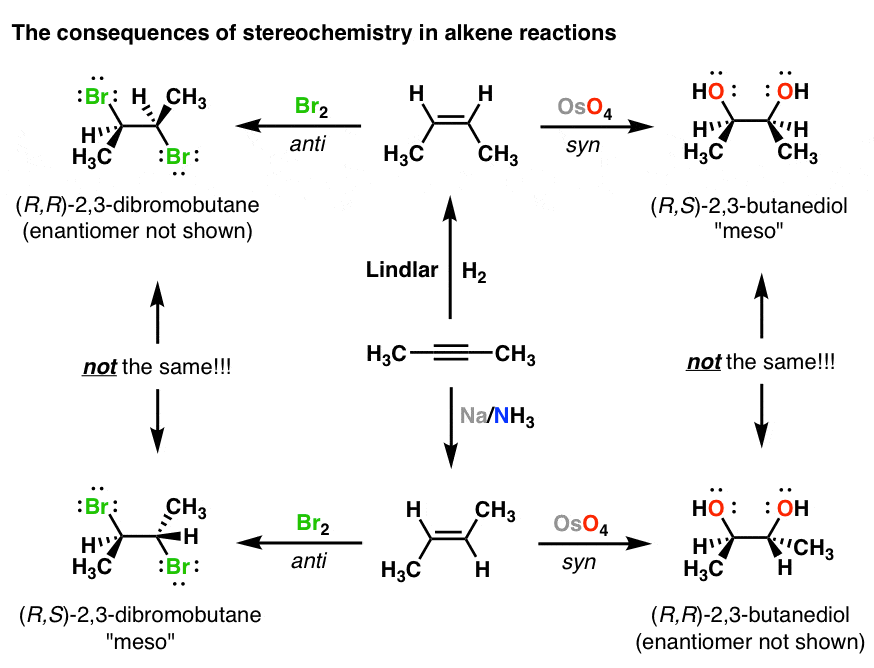
They have a lower heat of hydrogenation. The following illustrates stability of alkenes with various substituents. - More substituted alkenes are more stable - Trans alkenes are more stable than cis alkenes - The more stable an alkene the more exothermic the H f More Stable More - H f Less Stable Less - H f.
Lower energy molecules are more stable than higher energy molecules. C-C single bonds and C-H bonds. More substituted alkenes are more stable than less substituted ones due to hyperconjugation.
In disubstituted alkenes trans isomers are more stable than cis isomers due to steric hindrance. Therefore the extra bond is 38 kJmol 88 kcalmol weaker that an alkene. More substituted alkenes are more stable than less substituted ones due to hyperconjugation.
By definition alkenes are hydrocarbons with one or more carboncarbon double bonds R 2 CCR 2 while alkynes are hydrocarbons with one or more carbon-carbon triple bonds RCCR. Watch the next lesson. The unsubstituted alkene has no R groups to further stabilize it so it will be the least stable.
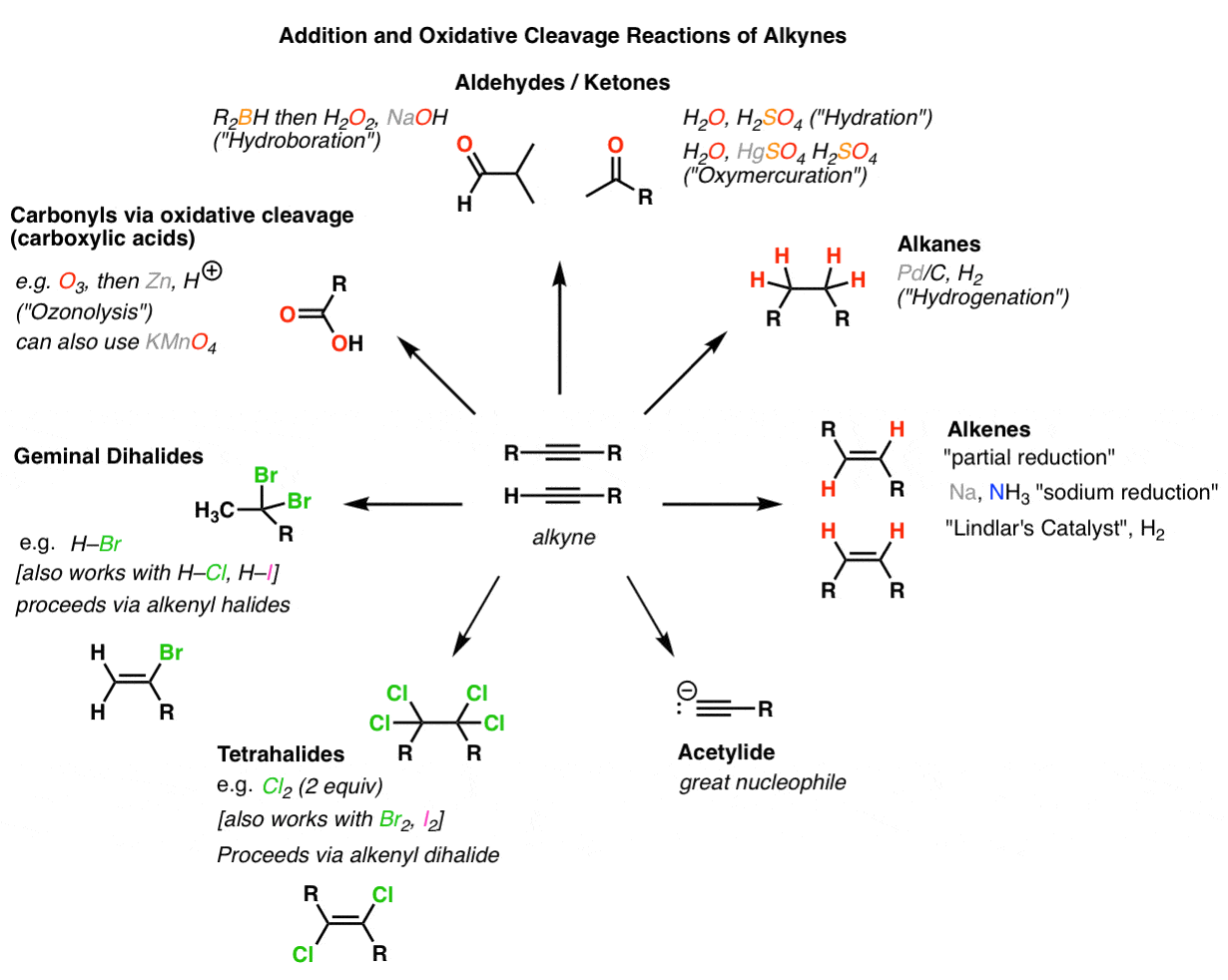
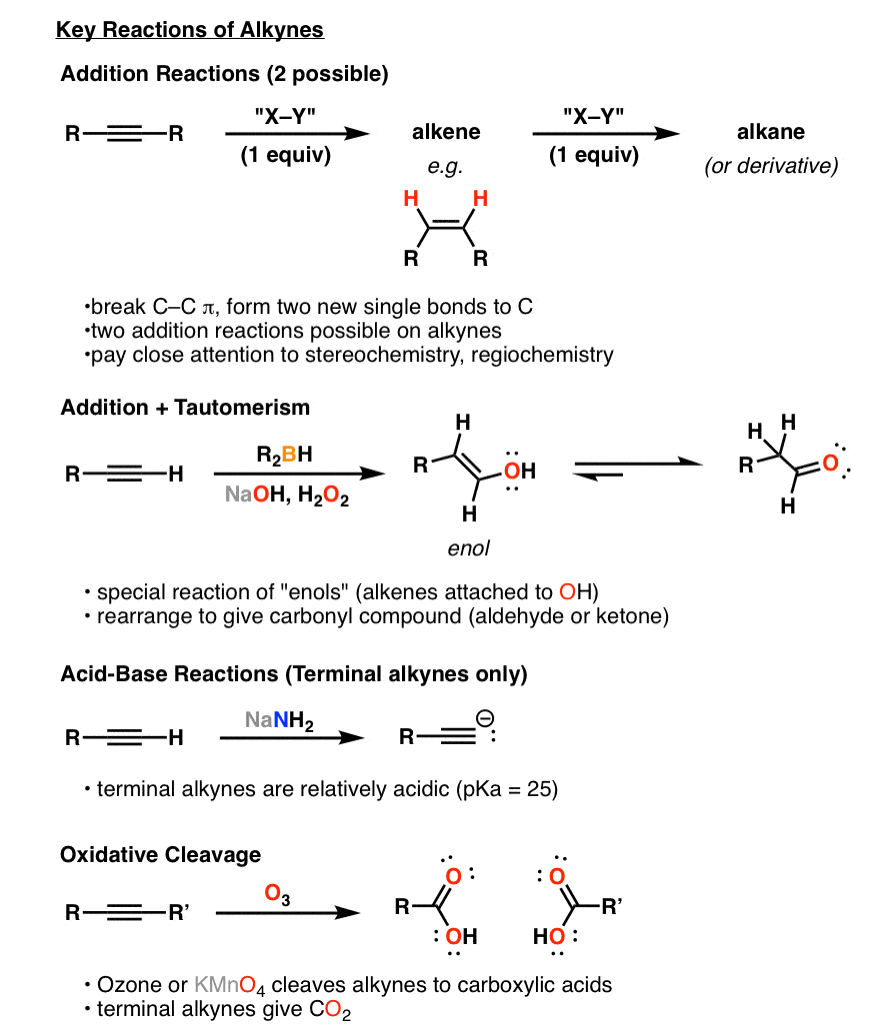
Synthesis 5 Reactions Of Alkynes Master Organic Chemistry
Ch105 Chapter 8 Alkenes Alkynes And Aromatic Compounds Chemistry

Stability And Reactivity Order Of Alkanes Alkenes And Alkynes Class 10 12 Organic Chemistry Youtube

Alkyne Reduction To Alkene And Alkane Organic Chemistry Study Chemistry Organic Chemistry


Post a Comment for "Alkene Vs Alkyne Stability"