Internal Alkene Definition Chemistry
Begingroup and an internal alkyne is in the center and an external alkyne is between the end and the center. An alkane is a saturated hydrocarbon.
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Internal Alkene
The chain is numbered to minimize the numbers assigned to the double or triple bond.

Internal alkene definition chemistry. The halide will add to the more substituted carbon following Markovnikovs rule. An alkenein which the carbon-carbon pi bondis at the end of the carbon chain. The product is a haloalkane also called an alkyl halide.
Like for example pent-2-yne or 2-pentyne is an external alkyne but pent-3-yne is an internal alkyne endgroup Caters May 23 15 at 2332. Alkenes are acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbons having one carbon-to-carbon double bond CC and the general molecular formula Cn H 2n 16. The hydrohalogenation of alkenes involves breaking a carbon to carbon double bond followed by the electrophilic addition of a hydrogen atom and halogen.
Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes due to the presence of the double bond. In general the -bond of an alkene is a much weaker base than the oxygen of a carbonyl so the hydrogen transfer is less efficient. Heres what you need to know about the branched alkanes.
Any of numerous unsaturated hydrocarbons having one double bond specifically. An alkene which is not terminal ie the carbon-carbon pi bond is not at the end of the carbon chain. Alkenes and alkynes are named by identifying the longest chain that contains the double or triple bond.
Any of a series of open-chain hydrocarbons CnH2n such as ethylene. Alkanes have the general chemical formula C n H 2n2. The cross-metathesis of unsaturated fatty acids esters with alkenes provides a useful route to synthesize unsaturated fatty acids with double bonds located at specific positions which may be difficult to synthesize by other methods.
The suffix of the compound is -ene for an alkene or -yne for an alkyne. Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry. Another term used to describe alkenes is olefins.
The Wacker-type oxidative alkene amination reaction is traditionally catalyzed by a palladium through a mechanism involving aminopalladation and -hydride elimination. The proximal C C unit functioned as the internal base and decarboxylation led to a 79 yield of 2 Z4 E-hexa-24-dienoic acid. In organic chemistry an alkane or paraffin a historical trivial name that also has other meanings is an acyclic saturated hydrocarbon.
In other words an alkane consists of hydrogen and carbon atoms arranged in a tree structure in which all the carboncarbon bonds are single. Definition of alkenes Acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbonshaving one carbon-carbon double bondand the general formulaCnH2n. Acyclic branched or unbranched hydrocarbonshaving more than one double bondare alkadienes alkatrienes.
Because alkenes contain less than the maximum possible number of hydrogen atoms per carbon atom they are said to be unsaturated. A copper-catalyzed oxidative amination of unactivated internal alkenes has been developed. Alkenes are a class of hydrocarbons eg containing only carbon and hydrogen unsaturated compounds with at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond.
Alkanes may be linear branched or cyclic.

Alkene An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Internal Alkene
Ch105 Chapter 8 Alkenes Alkynes And Aromatic Compounds Chemistry
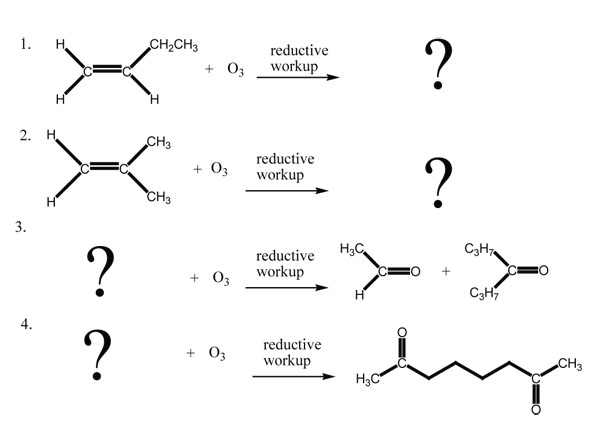
9 15 Oxidative Cleavage Of Alkenes Chemistry Libretexts
Why Are Alkenes Electron Rich Quora
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Internal Alkene
Illustrated Glossary Of Organic Chemistry Internal Alkene
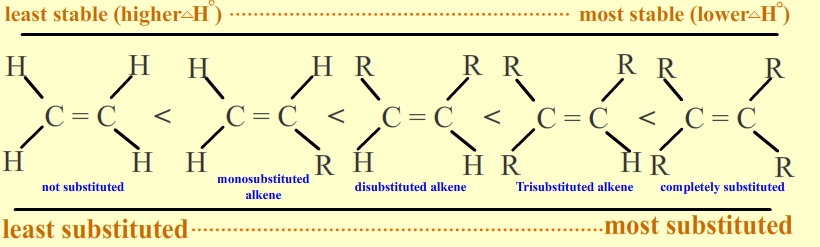
Post a Comment for "Internal Alkene Definition Chemistry"